Frontend Developer So You Built UI Then Backend Services: Bridging Design and Functionality Efficiently
- Jayant Upadhyaya
- Jul 22, 2025
- 9 min read

A frontend developer focuses on building the user interface, creating the visual elements and interactions that users engage with directly. Once the UI is complete, backend services come into play to handle data processing, store information, and ensure the application functions smoothly behind the scenes.
It is common to build the frontend UI first to visualize the design and user flow before integrating backend services that support its functionality. This approach helps identify missing features or necessary data requirements early, making backend development more targeted and efficient.
By separating these roles, developers ensure a clear division of labor: the frontend shapes user experience, while the backend supports that experience with reliable data and logic. This collaboration creates cohesive, responsive applications.
What Is a Frontend Developer?
A frontend developer focuses on building the user-facing parts of websites and web applications. This role involves translating design into interactive elements that users engage with, while ensuring functionality across devices and browsers. In companies like SynergyLabs, frontend developers often collaborate closely with backend teams to integrate visual features with server-side services.
Core Responsibilities in UI Development
Frontend developers are responsible for designing and coding the visual interface of websites. They work with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create layout, style, and interactive elements. This includes navigation menus, forms, buttons, and dynamic content.
They ensure that web pages are responsive, accessible, and consistent across various browsers and screen sizes. Testing and debugging are crucial parts of the workflow to maintain usability and performance.
Often, frontend developers integrate APIs and backend services to fetch and display data dynamically, enabling real-time updates and seamless user interactions.
Key Skills Required for Frontend Roles
Proficiency in HTML, CSS, and JavaScript forms the foundation of frontend development. Knowledge of frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.js is increasingly important for building scalable and maintainable user interfaces.
Understanding version control systems like Git supports collaboration in development teams. Familiarity with package managers (npm, Yarn) and build tools (Webpack, Babel) enhances workflow efficiency.
Frontend developers must also grasp UI/UX principles to create intuitive designs that meet user needs. Skills in debugging and performance optimization ensure smooth user experiences.
Soft skills such as communication and teamwork facilitate effective collaboration with designers and backend developers, especially in multidisciplinary environments like SynergyLabs.
Trends in Modern Frontend Development
Modern frontend development emphasizes component-based architectures to improve code reuse and maintenance. Frameworks like React popularized this approach, allowing granular control over UI elements.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are gaining traction by combining web features with native app-like experiences such as offline access and push notifications.
Tooling and automation are advancing rapidly, including CI/CD pipelines and automated testing to speed up development cycles without sacrificing quality.
Additionally, there's a growing focus on performance optimization, accessibility compliance, and security to provide better, safer user experiences across diverse platforms.
Designing User Interfaces
Effective user interface design balances aesthetics, usability, and functionality to create a seamless experience. It involves selecting appropriate tools, applying user experience principles, and structuring code to build maintainable and scalable UI elements. This approach ensures the UI supports both user needs and backend integration efficiently.
UI Frameworks and Libraries Overview
UI frameworks like Bootstrap and Material UI provide pre-built components such as buttons, modals, and tabs. These components speed up development by allowing developers to avoid reinventing common interface elements. They also ensure visual consistency and responsiveness across different devices.
Using these libraries promotes standardization while maintaining customization options for branding and user requirements. Frameworks typically include CSS, JavaScript, and often accessibility features out of the box. Leveraging them reduces development time for custom software and improves cross-browser compatibility.
UX Principles in Interface Design
User experience (UX) principles guide how interfaces should feel and function. Usability, accessibility, and clarity are fundamental. Designs must accommodate diverse users, including those with disabilities, by following guidelines like WCAG.
Emphasizing intuitive navigation and minimizing user effort increases engagement. Consistency in layout and feedback mechanisms builds trust. Prioritizing speed and reducing unnecessary complexity ensures users can complete tasks efficiently, making the software practical and effective.
Component-Driven Development
Component-driven development breaks the UI into independent, reusable parts. Each component manages its own logic and styling, making updates and debugging more straightforward. This modularity aligns closely with modern front-end frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular.
By reusing components across projects, developers accelerate UI assembly and maintain consistent behavior. This approach supports scaling complex custom software, where interfaces evolve over time. It also facilitates collaboration between designers and developers by creating clear separation between visual elements and application logic.
Integrating Backend Services With Frontend
Connecting frontend interfaces with backend services requires precise communication channels, well-implemented security, and the ability to handle live data updates. These elements ensure that applications, including SaaS and mobile apps, are responsive, secure, and efficient.
API Communication and Data Fetching
Backend services typically expose APIs, most commonly RESTful or GraphQL, that frontend developers use to exchange data. The frontend sends HTTP requests to these API endpoints to fetch or modify data. Popular JavaScript libraries like Axios or native fetch are commonly used for this purpose.
Frontend frameworks such as React or Angular manage asynchronous data fetching by handling promise responses and updating the user interface accordingly. Clear API documentation and consistent endpoint design simplify development and reduce integration errors.
Efficient data fetching also includes caching strategies and error handling to improve user experience and minimize server load. Full-stack developers often design APIs that return only the necessary data to keep responses lightweight.
Authentication and Security Integration
Secure communication between frontend and backend is vital, especially for SaaS platforms handling sensitive user data. Authentication methods often use tokens such as JWT (JSON Web Tokens) that the frontend includes in API requests.
Backend validates these tokens before granting access to protected resources. Frontend must securely store tokens, frequently in HTTP-only cookies or secure storage mechanisms to prevent XSS attacks.
Additionally, HTTPS is mandatory to encrypt data transmitted between frontend and backend. Role-based access control (RBAC) handled server-side ensures users can only perform actions permitted by their authorization level.
Real-Time Data Handling
For mobile apps or dynamic SaaS dashboards, real-time updates enhance interactivity. Backend services integrate with frontend using WebSockets or protocols like GraphQL subscriptions for live data streams.
WebSockets establish persistent connections allowing the server to push updates instantly. This reduces the latency of data changes in UI compared to periodic polling.
Implementing real-time communication requires careful management of connection states and fallback strategies to maintain reliability. Full-stack developers optimize these systems to balance performance with server resource use.
From UI to Backend: The Developer’s Journey

A developer moving from UI design to backend services must adapt to new tools, languages, and project dynamics. This shift requires understanding how user-facing elements interact with server logic and databases. Mastery of both layers improves development efficiency and helps deliver more cohesive applications.
Understanding Full-Stack Workflows
Full-stack workflows combine frontend and backend tasks into a single development cycle. Developers manage UI components like buttons, forms, and layouts, while also handling backend concerns such as database queries, authentication, and API endpoints.
In an agile consultancy environment, this approach promotes frequent iterations and faster feedback by allowing a single developer or team to address client requirements end-to-end. Common backend languages include Node.js, Python, and Java, which integrate with frontend frameworks like React or Vue.
Benefits of full-stack workflows:
Reduced dependency delays
Streamlined communication
Faster prototyping and troubleshooting
Developers also often implement CI/CD pipelines to automate deployment, including ML/ML Ops practices to integrate machine learning models with the backend when necessary.
Bridging the Gap Between Frontend and Backend
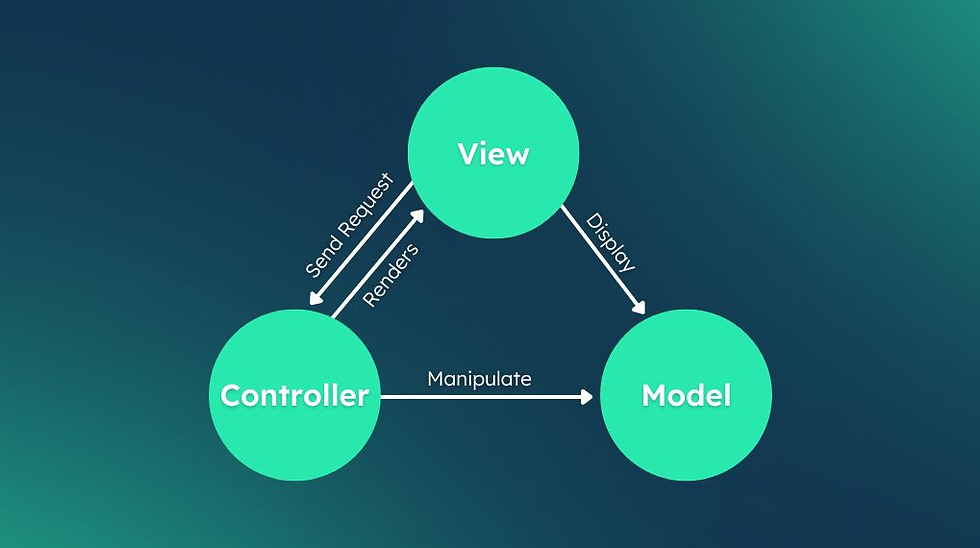
Bridging frontend UI and backend services involves clear communication between components via APIs, primarily RESTful endpoints. The frontend sends requests to the backend, which processes data and returns responses that update the UI in real time.
Understanding data flow is crucial. Developers need to map user actions to backend logic, ensuring security, validation, and error handling are enforced at the server level. Familiarity with tools like Postman or Swagger aids in testing these interfaces.
In practice, frontend code handles presentation and client-side logic while backend services manage data persistence, authentication, and business rules. Successful integration relies on consistent API design, often documented and maintained during agile sprints to align with evolving project scopes.
Collaboration and Product Discovery
Effective collaboration is essential to ensuring that UI development aligns with backend services and overall product goals. Close communication helps teams clarify requirements, identify risks early, and validate assumptions to create functional, user-centered products.
Cross-Functional Teamwork
Cross-functional teams bring together UI designers, frontend developers, backend engineers, and product managers to streamline product discovery. Each role contributes unique insights—designers focus on user experience, frontend developers on interaction and presentation, and backend developers on data handling and business logic.
Regular syncs and shared tools, such as design systems or API documentation, reduce misunderstandings. For example, a frontend developer relies on finalized Figma designs as a contract for UI components, while backend developers build APIs based on agreed specifications. This approach minimizes improvisation and accelerates development cycles.
Prioritizing open communication channels enables quick resolution of integration issues and fosters deeper understanding of technical constraints and user needs. Such teamwork supports continuous alignment throughout both UI and backend construction.
Agile Methodologies in Practice
Agile frameworks like Scrum or Kanban facilitate iterative product discovery by encouraging frequent collaboration and incremental delivery. Teams work in short cycles, allowing for rapid feedback on UI prototypes and backend functionality.
Daily stand-ups, sprint planning, and retrospectives give visibility into progress and roadblocks for both frontend and backend tasks. This transparency helps adapt priorities based on user testing results or technical dependencies.
In Agile teams, product owners actively collaborate with developers to refine user stories, ensuring that frontend features match backend capabilities. This tight coordination prevents scope creep and enables timely delivery of a coherent product aligned with business goals.
Case Studies: Industry Applications
Frontend developers often create intuitive interfaces before integrating backend services to enable complex features. This approach supports various industries by focusing on user experience while ensuring robust data handling and performance.
Logistics Platform Development
In logistics, frontend developers design dashboards that visualize supply chain data clearly and responsively. Users benefit from real-time updates on shipment status, route optimization, and inventory levels.
Backend services process large data streams, often enhanced by AI-powered video analytics, to monitor packaging and loading operations. This integration improves accuracy and operational efficiency.
The frontend-backend collaboration allows rapid adjustments to delivery schedules via automated notifications, enabling logistics companies to respond swiftly to delays or disruptions.
E-Commerce Interface Solutions
E-commerce platforms require seamless product browsing, intuitive checkout processes, and personalized recommendations. Frontend developers focus on responsive designs that function across devices, improving conversion rates.
Backend systems handle real-time inventory updates, payment processing, and customer data management. Advanced APIs support personalization algorithms that increase user engagement based on purchase history.
Scalable architecture ensures that the platform accommodates traffic spikes during sales events, maintaining performance without downtime or slow loading times.
Fintech and Real-Time Analytics
In fintech, frontend interfaces display complex financial data in user-friendly charts and dashboards. Developers emphasize security and clarity to facilitate quick, accurate decision-making.
Backend services power real-time analytics and transaction processing, ensuring data consistency and compliance with financial regulations. Integration with external APIs provides live market data and risk assessments.
The combination of strong frontend design and backend reliability supports mobile banking apps, trading platforms, and AI-driven credit scoring, enhancing transparency and user trust.
Choosing the Right Technology Stack

Selecting the appropriate tools for both the user interface and backend services is critical in building reliable custom software. The right choices improve development speed, maintainability, and user experience while reducing technical debt. Key factors include performance, compatibility, and scalability.
Front-End Tooling Selection
Front-end tooling must balance functionality and usability. Developers often prioritize frameworks like React, Vue, or Angular for their component-based structure and community support. These tools offer reusable components and facilitate responsive, dynamic interfaces.
Performance is crucial. Tools should minimize load times and handle complex interactions smoothly. Compatibility with emerging web standards and browsers ensures longevity. Additionally, ease of integration with backend APIs and state management solutions like Redux or Vuex supports complex app logic.
Tooling that supports developer productivity, such as hot-reloading and debugging capabilities, also matters. For custom software, adaptability to specific UI requirements and flexibility in styling, including CSS-in-JS or modular CSS, should be considered.
Evaluating Backend Solutions
Backend tools power application logic, data management, and integrations. Choosing between environments like Node.js, Django, or Spring Boot involves assessing project scale, language familiarity, and community ecosystem.
Scalability is vital. Backend frameworks should handle increasing requests without significant performance loss. Database compatibility—SQL or NoSQL—also drives backend choice, influencing data handling efficiency.
Security and maintainability are non-negotiable. Features such as built-in authentication libraries, support for microservices architecture, and easy API endpoint creation streamline development and protect data.
Finally, seamless interaction between backend and front-end services through RESTful or GraphQL APIs ensures reliable data flow and better user experience in custom software projects.
Future Trends for Frontend Developers
Frontend development now integrates advanced technologies that redefine how user interfaces and backend services interact. These shifts bring new tools and roles that require developers to expand their skill sets, especially around AI integration and full-stack proficiency.
The Rise of AI in UI/UX
AI is becoming a core element in frontend development, enhancing UI/UX through personalized, data-driven interfaces. Tools developed by firms like SynergyLabs in India drive the adoption of AI-powered design systems that automate layout adjustments and optimize user interactions based on behavior analytics.
Moreover, AI facilitates rapid prototyping and testing by predicting user preferences and automating routine coding. Frontend developers leverage ML Ops to deploy machine learning models that improve accessibility and responsiveness in real-time. This means interfaces can adapt dynamically without extensive manual intervention, improving performance and user satisfaction.
Opportunities in Full-Stack Development
Frontend developers increasingly engage with backend services, merging responsibilities to become full-stack practitioners. This trend demands fluency in server-side languages, APIs, and databases alongside UI frameworks.
Mastery of backend integration allows developers to build seamless, end-to-end experiences, controlling data flow and performance more tightly. It also opens opportunities in cloud-based environments and containerized deployments, areas boosted by advancements in ML Ops practices.
By incorporating backend logic early, developers reduce dependencies and improve feature delivery speed. Teams like SynergyLabs focus on hybrid roles that blend frontend creativity with backend engineering, reflecting this evolving industry standard.



Comments